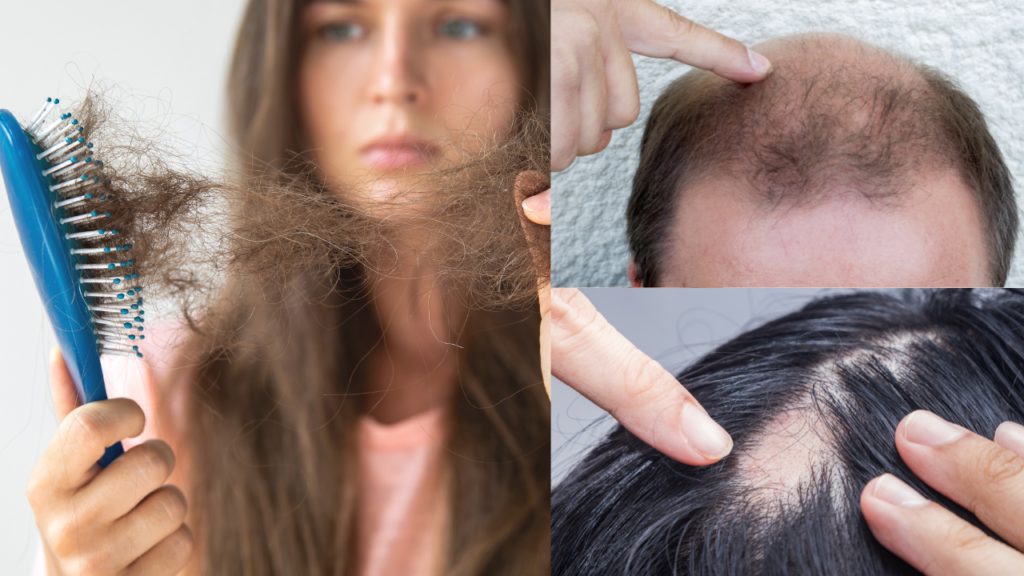
Today, I delve into a crucial topic that many will encounter in their lives: hair loss, also known as alopecia. Hair loss significantly impacts the self-esteem of both men and women. Therefore, it’s essential to take action at the first signs of hair loss to identify the cause and initiate appropriate treatment. Unfortunately, many first experiment with various over-the-counter remedies and shampoos, delaying seeking medical help until later stages.
In this blog post, I’ll explore the most common causes of hair loss, shedding light on each aspect. Subsequently, I’ll delve into potential treatments in a follow-up post. For consultations and treatments specializing in hair loss, you can visit my clinic, Doctor Contour Clinic, located in Antwerp, Belgium.
VIDEO:
Categories of Alopecia
- Non-scarring alopecia: In this type, the hair follicles remain intact, and the damage is not permanent, meaning the hair has the potential to regrow. Conditions in this category include telogen effluvium, androgenetic alopecia (also known as female and male pattern baldness), and alopecia areata.
- Scarring alopecia: In this form, the hair follicle is destroyed and replaced by scar tissue, preventing hair from regrowing. Examples of this are discoid lupus erythematosus.
- Hair shaft abnormalities: In these cases, hair loss is not characterized by hair falling out, but by abnormalities in the structure of the hair shaft, causing the hair to break more easily.
Signs of Hair Loss
The two most common signs of hair loss are hair shedding and hair thinning.
- Hair shedding is often noticeable during showering, when it seems like hair is falling out everywhere.
- Hair thinning becomes visible over time through increased scalp visibility. Most people do not notice hair thinning until they have lost about 50% of their hair.

There are various causes of hair loss, such as genetics, medication, environmental factors, deficiencies in minerals or vitamins, stress, and more. It is important to remember that hair loss becomes abnormal when the shedding and thinning significantly deviate from what is normal for you.
Most Common Causes of Alopecia
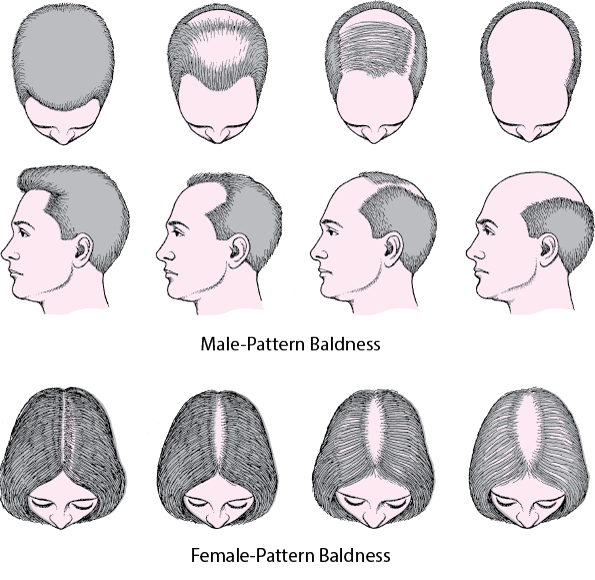
1. Androgenetic Alopecia

Androgenetic alopecia, also known as male or female pattern baldness, is a common form of hair loss caused by genetic and hormonal factors. This type of hair loss often manifests differently in men and women.
In men, it typically results in a receding hairline and thinning hair on the crown, while women experience a wider parting on the scalp and overall thinning hair.
It is a misconception that this form of alopecia only occurs in men over 40 and women after menopause; it can occur at any age, even in the twenties or thirties. Additionally, in women, polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) should always be ruled out as a possible cause, especially if hair loss is accompanied by irregular menstruation, excessive hair growth on the face, back, and abdomen, acne, and other symptoms.
2. Telogen effluvium
Telogen effluvium, also known as stress-induced hair loss, occurs when an abnormal number of hair follicles transition from the growth phase to the resting phase of the hair growth cycle in response to extreme stressors. This results in increased hair shedding and can be caused by weight changes, recent surgeries, illness, or other stressful events. Telogen effluvium can also occur after pregnancy, leading to significant hair loss and thinning hair in many women several months after giving birth.

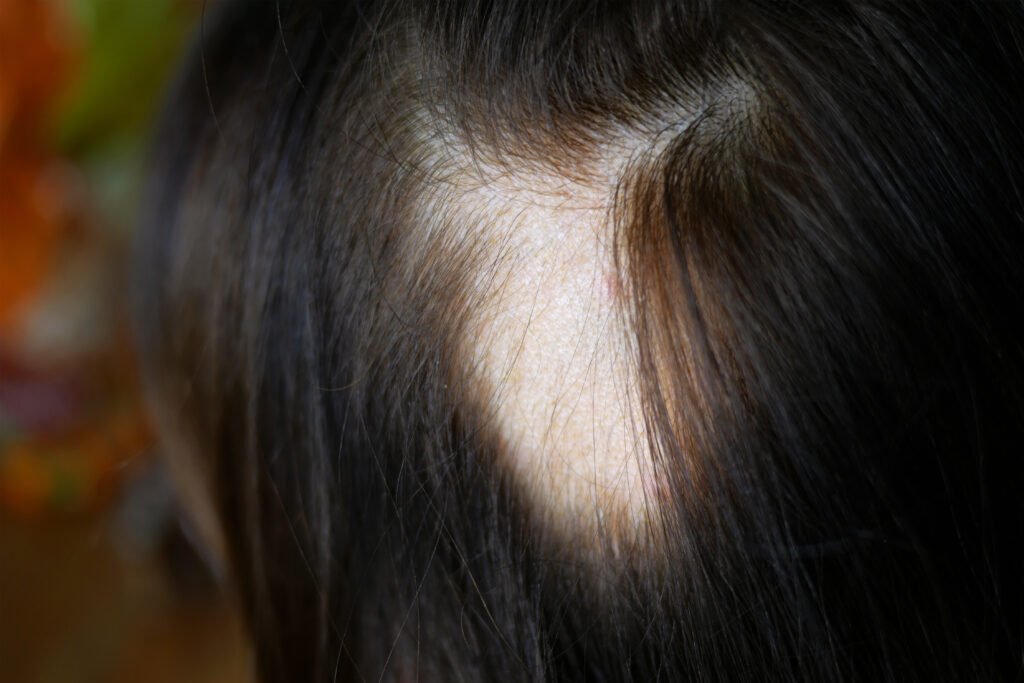
3. Alopecia Areata
Alopecia areata is caused by an autoimmune reaction in which the immune system attacks hair follicles, resulting in sudden hair loss in small round patches on the scalp or elsewhere on the body. Although the exact cause is not fully understood, genetics and stress may play a role. Treatment, such as corticosteroid injections into the scalp, can help some people promote hair growth, but the regrowth of hair is not guaranteed.
4. Medical conditions
Various medical conditions can cause hair loss. It is important to rule out these conditions in individuals with hair loss to provide the appropriate treatment:
- Hypothyroidism: An underactive thyroid can lead to hair loss by disrupting the hormonal balance in the body. This can result in thinning hair and hair loss across the entire scalp.
- Lupus: Lupus is an autoimmune disease where the immune system attacks healthy tissues, including hair follicles. This can lead to patchy hair loss on the scalp, known as alopecia areata.
- Iron deficiency: A lack of iron in the body can cause anemia and hair loss. This is often seen in young women with heavy menstrual periods, as they lose more iron than they can replenish, resulting in thinning hair and hair loss.
- Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS): In women with PCOS, hormonal imbalances can lead to the overproduction of male hormones, causing hair loss, particularly on the crown of the head.
- Skin conditions: Some skin conditions, such as seborrheic dermatitis and psoriasis, can also cause hair loss due to inflammation and irritation of the scalp.
5. Medications
Certain medications can cause hair loss as a side effect. Consulting a doctor is essential if you suspect that a medication is causing hair loss.
Possible medications that can cause hair loss include:
- Chemotherapy: Affects rapidly dividing cells, including hair follicles, resulting in hair loss.
- Birth control pills: Some variants can cause hormonal changes that lead to hair loss as a side effect.
- Antidepressants: Certain antidepressants can cause temporary hair loss during use.
- Blood thinners: Medications such as warfarin and heparin can cause hair loss as a side effect.
- Medications for heart problems and high blood pressure: Beta-blockers and ACE inhibitors are some examples that can cause hair loss.
- Anticonvulsants: Medications used for epilepsy, such as phenytoin, can cause hair loss.
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs): Pain relievers such as ibuprofen and aspirin can cause hair loss with prolonged use.

6. Traction alopecia
Traction alopecia occurs due to repeated tension on the hair follicles, caused by tight hairstyles such as tight ponytails, braids, or extensions. This constant tension can lead to hair breakage and even permanent hair loss in the affected areas. To prevent further damage, it is important to regularly vary your hairstyles and ensure that your hair is not continuously under tension.

7. Trichotillomania
Trichotillomania is an impulse control disorder where a person has an irresistible urge to pull out their own hair. This condition is often caused by stress, anxiety, or other emotional issues and serves as a way to cope with negative or uncomfortable feelings.
People with trichotillomania often have hairs in various stages of regrowth, as the hairs are pulled out at different times. This results in an uneven pattern of hair lengths in the affected areas. It is important for individuals suffering from trichotillomania to seek professional help, such as cognitive behavioral therapy, to address the underlying causes and learn to manage the urge to pull out hair.

Conclusion
It is important to remember that this blog post is for informational purposes only and does not substitute for medical advice.
If you are experiencing hair loss, it is essential to consult a doctor for a proper diagnosis and treatment.
If you want to learn more about hair loss and possible treatments, you can make an appointment at our clinic, Doctor Contour Clinic, in Antwerp, Belgium. There is also the option to take the Trichotest, a DNA analysis to find the appropriate treatment for your hair loss, so you don’t waste any extra time. As mentioned earlier in this blog post, it is important to act as quickly as possible if hair loss occurs. This way, we can work together to treat your hair loss, stop further hair loss, and possibly grow new hair for a beautiful head of hair.

